- Apr. 05, 2024
- Public Relations
Development of a Wastewater Biomarker Sensor for Real-Time Detection of Infectious Disease Trends - Adopted as Part of the FY2024 B-DASH (Feasibility Study) by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism
Nihon Suido Consultants Co., Ltd. together with MEIDENSHA CORPORATION (Representative Director, President and Executive Officer INOUE Akio), UNIADEX, Ltd. (PRESIDENT & CEO TANAKA Ken), SANKI ENGINEERING CO., LTD. (Representative Director & President ISHIDA Hirokazu), NSC TEC Co., Ltd. (Representative Director and President OSUMI Hidetoshi), the Graduate School of Engineering of Tohoku University (President TOMINAGA Teiji), and Sendai City (Mayor KORI Kazuko) submitted a proposal for the “FY2024 B-DASH (Feasibility Study) by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism,” and the proposal was adopted on March 28, 2024.
Key Points of Presentation
- “Identification of wastewater biomarkers to track patients with infectious diseases”: We will address the identification of in-wastewater biomarkers for COVID-19 infections, seasonal influenza, infectious gastroenteritis, and RS virus infections.
- “Development of real-time monitoring sensors for wastewater biomarkers”: We will develop biosensors to detect infectious disease-related biomarkers in wastewater.
- “Construction of a real-time wastewater information sharing system”: We will work to immediately display the results of infectious disease-related detections by the wastewater biomarker sensor on the wastewater information sharing DX platform (already constructed through an FY2022 Cabinet Office project*).
*Demonstration of a sustainable system for the effective use of wastewater information and its application by municipalities (Cabinet Secretariat, FY2022)
Outline of Research
Wastewater survey findings are currently being applied worldwide to monitor infectious disease trends. However, the concentration of viruses in wastewater is generally very low and detection requires concentration, gene extraction, and amplification. As a result, the monitoring of infectious disease trends lacks capacity for real-time detection. This research will develop sensor technology to detect infectious disease-related protein biomarkers, which are present in wastewater at higher concentrations than viruses, and integrate IoT technology to enable real-time monitoring of infectious disease information from wastewater.
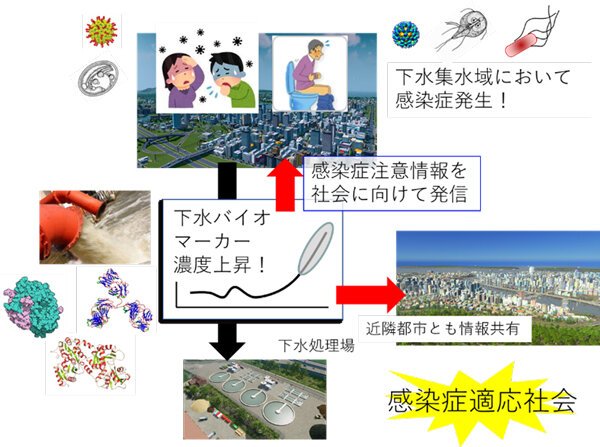
Conceptual diagram of a society adapted to infectious diseases to be established in this research
Role of Each Organization
The main roles of each organization are as follows.
| Nihon Suido Consultants Co., Ltd. | Principal investigator, organizing epidemiological data, wastewater proteome analysis (comprehensive identification of proteins in wastewater) |
| MEIDENSHA CORPORATION | Development of a wastewater biomarker sensor and real-time information sharing system |
| UNIADEX, Ltd. | Development of a real-time information sharing system |
| SANKI ENGINEERING CO., LTD. | Organizing epidemiological data, wastewater proteome analysis |
| NSC TEC Co., Ltd. | Organizing epidemiological data, wastewater proteome analysis |
| Tohoku University | Identification of wastewater biomarkers, development of wastewater biomarker sensors |
| Sendai City |
Provision of wastewater samples and demonstration experiment sites |
Future Development
The Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism has been pushing the application of wastewater information as a national policy, including the development of guidelines for the use of wastewater information. The results of this research have significant advantages in terms of real-time performance and cost compared to conventional methods, and we believe that the application of wastewater information is expected to become even more established and widespread. The joint research team, including our company, will continue to promote research with the aim of adding further value to wastewater information.
Reference
Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism:
